Sun Exposure Time versus Vitamin D Intake

I researched the equivalent sun exposure time versus vitamin D levels. In other words, how to cross-reference sun on the skin compared to how much vitamin D supplement (mcg—micrograms, or IU—International Units) you would need to take if you were hardly exposed to the sun (winter months)?
I was curious about this because I know how important vitamin D is for our Immune System Health! Plus, my bloodwork had indicated slightly low D levels (most people don’t realize how common this is).
There are many benefits of vitamin D. You can look it up. Here’s one study that you might find interesting:
“A systematic review and meta-analysis of 14 observational studies that included a total of 31,424 adults (mean age ranging from 27.5 to 77 years) found an association between deficient or low levels of 25(OH)D and depression [source: British Journal of Psychiatry]
Most People Do Not Get Enough Vitamin D
More than 40% of American adults are estimated to have a vitamin D deficiency [source: NIH National Library of Medicine].
It’s estimated that as many as half of all children, teens, and young adults are vitamin D deficient, as are as many as 25 to 57 percent of American adults [source: Lee]
Vitamin D deficiency is very common.
Why People Don’t Get Enough Vitamin D
Many reasons for this include:
- Partly due to vigilant sun protection, since sunscreen with SPF 30 reduces vitamin D production by 95%.
- The majority of people in the United States (for example) do not get any vitamin D from the sun during the winter months—zero. There are exceptions at southern latitudes.
- In the U.S., nearly everyone is deficient while living above 37 degrees north of the equator—that’d put you north of Washington, D.C., and north of the Utah/Arizona border.
- The darker your skin pigment, the less UVB rays can penetrate.
- Overweight and Obesity. Vitamin D is fat-soluble. The more fat cells your body has, the more at risk you are of a deficiency, because the vitamin becomes trapped in those fat cells.
- Most people are “inside” most of the day in our modern world.
- Kids don’t “play outside” like they used to.
- Although one needs to be cautious about overdoing sun exposure (given the well-known risks), many people are seemingly petrified of the sun these days.
- Age. As we age, it naturally becomes more difficult to convert sunlight into D3. For example, when exposed to the same amount of UVB radiation, a 70-year-old will make 75 percent less D3 than a 20-year-old.
I may earn commission (no extra cost) if purchased.
Thank you
Dr. Berg Vitamin D3 & K2
Many consider this one among the best vitamin D supplements due to its absorption properties and its well-known, highly rated USA business.

Search all Vitamin D3 & K2 on Amazon
How Much Vitamin D Should I Take?
Since 2010, the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of vitamin D falls between 600 and 800 International Units (IU) per day (based on age).
However, more recent research suggests that adults may need at least 2,000 IU of vitamin D daily to maintain a healthy level in the body and reap the most benefits [source: MayoClinic, Holick].
I take plenty of vitamin D supplements during the Fall, Winter, and Spring months, but I’m curious how much I might get naturally from the sun during the summer months.
I used to take 5,000 IU per day, and now I take 10,000 IU per day. That is not medical advice. It’s simply what I do based on my lab results from annual checkups.
How Vitamin D Gets Into The Body From The Sun
The simple explanation:
The sunshine vitamin is made from cholesterol in your skin when exposed to the sun.
When your skin is exposed to sunlight, it makes vitamin D from cholesterol.
The sun’s ultraviolet B (UVB) rays hit cholesterol in skin cells, providing the energy for vitamin D synthesis.
~ healthline
The technical detailed explanation:
When UVB rays hit your skin, a chemical reaction happens:
Your body begins converting a prohormone in the skin into vitamin D. In this process, a form of cholesterol called 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC), naturally found in your skin, absorbs UVB radiation and is converted into cholecalciferol. Cholecalciferol is the previtamin form of D3.
Next, the previtamin travels through your bloodstream to your liver, where the body metabolizes it. It turns into hydroxyvitamin D, which is also known as 25-hydroxyvitamin D or 25(OH)D.
The kidneys then convert the 25(OH)D into dihydroxyvitamin D, also called 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D or 25(OH)2D. This is the hormone form of vitamin D that your body can use.
[sources: The George Mateljan Foundation, Holick]
Vitamin D produced from the skin can last at least twice as long as the vitamin D you take through foods or supplements.
A study in Norway found that ” under picture-perfect conditions, the human body is able to produce as much as 10,000 IU to 20,000 IU of vitamin D3 in just 30 minutes.”
How Much Time In The Sun To Get 4,000 IU
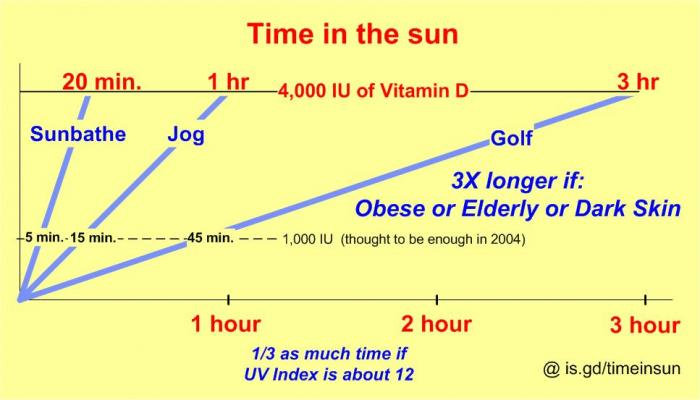
You can do your due diligence on this if you’d like. There’s a lot of info out there. I did find this particular resource interesting. It coincides similarly with other general data.
Interpreting the chart above…
Twenty minutes “sunbathing” may be approximately equivalent to about 4,000 IU of vitamin D. That’s obviously with a lot of exposed skin (and no sunscreen). After that initial exposure time, I would certainly apply sunscreen!
About 1 hour “jogging” in the sun equates to about 4,000 IU of vitamin D. I presume a ‘normal’ amount of exposed skin on the arms, legs, and face. Probably wearing shorts.
Adjust the times above by one-third if the UV Index is about 12 (which is very high).
Adjust the times above by 3X if you’re elderly, obese, or have dark skin.
The Best Time Of Day For Vitamin D From The Sun
Midday is the best time, as the sun is at its highest point, and your body can manufacture it most efficiently.
“If your shadow is longer than your body height, you can’t make any vitamin D. “Between 10 a.m. and 3 p.m. is the usual window for significant sun exposure [source: Holick]
Interesting factoid:
The amount of UVB radiation available depends on the angle at which the sun’s rays strike the Earth. Because of the effect of the sun’s angle, even in clear skies, synthesis of vitamin D in the skin is impossible for four months of the year in Boston, Massachusetts (for example).
[ Read: My Daily Vitamin Supplements For Health and Well Being]


I take Dr Berg 10,000 iu vitamin D3 & K2 once a day… 💪